Location: Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh
Our Work
In India’s governance structures, districts play a critical role in driving last mile reform implementation in our classrooms. Focussing on districts as the unit of change, CSF’s District Project Management Units (DPMUs) have emerged as a key catalyst in driving district-level implementation of the state FLN missions. We work with education officials, mentors and teachers to drive implementation fidelity, leading to improvement in student learning outcomes at both the district and state levels. Anchored in structured guidelines, capacity building and robust monitoring, this approach strengthens classroom delivery, drives measurable improvements in student learning and creates scalable models for system-wide adoption.
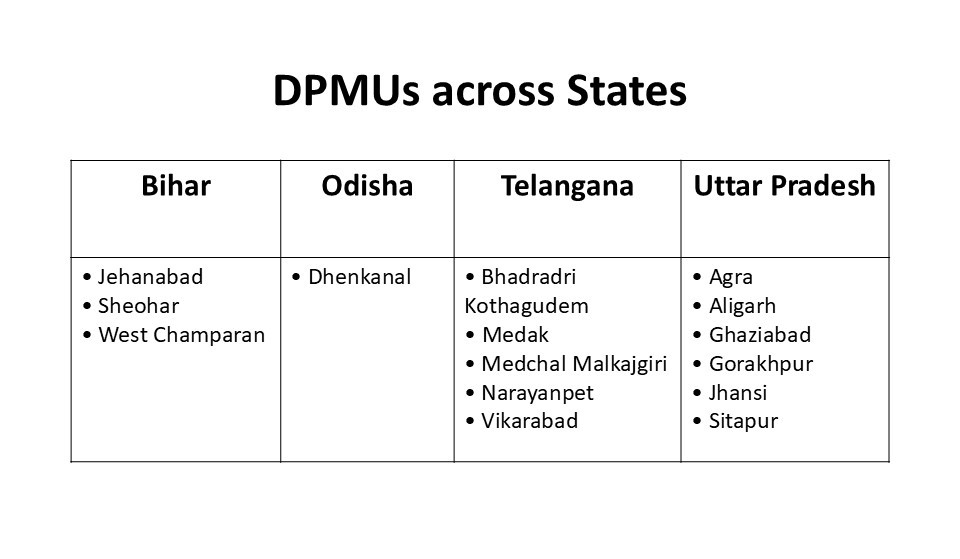
Driving Impact on the Ground
Pillars of our DPMU Strategy
CSF-led DPMUs work across five key pathways to build systems and enable district teams for effective FLN implementation.
Our Approach to Drive Deeper Classroom Impact
Each DPMU supports districts to strengthen core teaching-learning processes, guided by an iterative model focussed on improving teacher practice, data monitoring and Mission adoption.

